Il Est: A Deep Dive into French Language Nuances
Introduction
“Il est” is a common phrase in French, meaning “he is” or “it is.” It’s fundamental in the French language and is used in various contexts. Understanding its usage is crucial for anyone learning French, as it appears frequently in conversations, literature, and media. In this blog post, we will explore different aspects of “il est,” its grammatical importance, common uses, and how it enhances communication in French.
The Basics of “Il Est”
“Il est” is composed of the pronoun “il” (he or it) and the verb “être” (to be). It is used to describe people, things, and time. For example, “Il est gentil” (He is kind) or “Il est huit heures” (It is eight o’clock). This simple phrase forms the foundation of many sentences in French.
Describing People with “Il Est”
One of the most common uses of “il est” is to describe a person’s attributes or characteristics. For instance, “Il est intelligent” (He is intelligent) or “Il est médecin” (He is a doctor). This usage helps in identifying and describing individuals in a concise manner.
Describing Objects with “Il Est”
“Il est” is also used to describe objects and their states. For example, “Il est cassé” (It is broken) or “Il est neuf” (It is new). This application is essential for talking about the condition or state of things.
Telling Time with “Il Est”
Telling time is another critical use of “il est.” In French, time is often expressed using this phrase, such as “Il est midi” (It is noon) or “Il est minuit” (It is midnight). Understanding this usage is vital for everyday conversations about time.
Weather Expressions with “Il Est”
Weather expressions frequently use “il est” to describe current conditions. For example, “Il est chaud” (It is hot) or “Il est froid” (It is cold). These expressions are common in daily conversations and weather reports.
“Il Est” in Formal Writing
In formal writing, “il est” is used to present facts or describe situations. For example, “Il est nécessaire de suivre les règles” (It is necessary to follow the rules). This usage highlights the importance of clarity and precision in written communication.
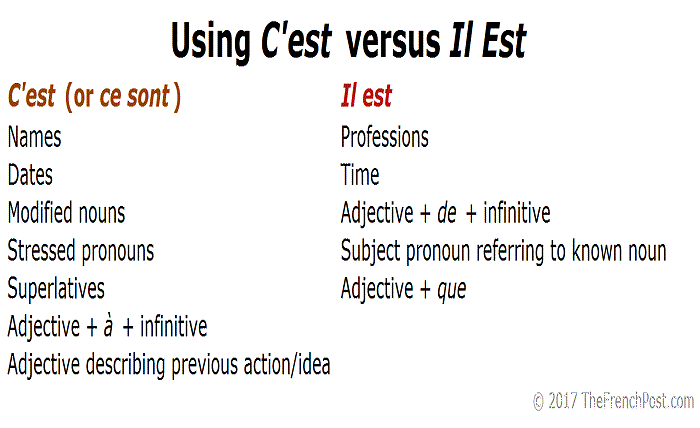
Differences Between “Il Est” and “C’est”
Understanding the difference between “il est” and “c’est” is crucial for mastering French. “Il est” is used with adjectives, professions, and times, while “c’est” is often used with nouns. For example, “Il est professeur” (He is a teacher) vs. “C’est un professeur” (He is a teacher).
Common Mistakes with “Il Est”
Learners of French often make mistakes with “il est.” Common errors include using it incorrectly with nouns or confusing it with “c’est.” For example, saying “Il est un bon” instead of “C’est un bon.” Recognizing and correcting these mistakes is key to fluency.
Cultural Significance of “Il Est”
“Il est” holds cultural significance in French-speaking countries. It reflects the language’s structure and the importance of concise expression. Understanding its use can enhance one’s appreciation of French culture and communication styles.
Practicing “Il Est” in Conversation
Practice makes perfect. Engaging in conversations using “il est” helps reinforce its correct usage. Examples include discussing daily routines, describing people and objects, and talking about the weather. Regular practice will lead to greater confidence and fluency.
Conclusion
“Il est” is a fundamental phrase in French that serves various purposes, from describing people and objects to telling time and discussing the weather. Mastering its use is essential for effective communication in French. By understanding its nuances and practicing regularly, learners can improve their fluency and appreciation of the French language.
FAQs
1. What does “il est” mean in French?
“Il est” means “he is” or “it is” in French, and it is used to describe people, objects, and time.
2. How is “il est” used to tell time in French?
“Il est” is used to tell time by stating the hour, such as “Il est dix heures” (It is ten o’clock).
3. Can “il est” be used to describe weather?
Yes, “il est” can describe weather conditions, like “Il est ensoleillé” (It is sunny) or “Il est pluvieux” (It is rainy).
4. What is the difference between “il est” and “c’est”?
“Il est” is used with adjectives and professions, while “c’est” is used with nouns. For example, “Il est professeur” (He is a teacher) vs. “C’est un professeur” (He is a teacher).
5. How can I practice using “il est” effectively?
Practice using “il est” in daily conversations, describe people and objects, tell time, and talk about the weather to reinforce its correct usage.




